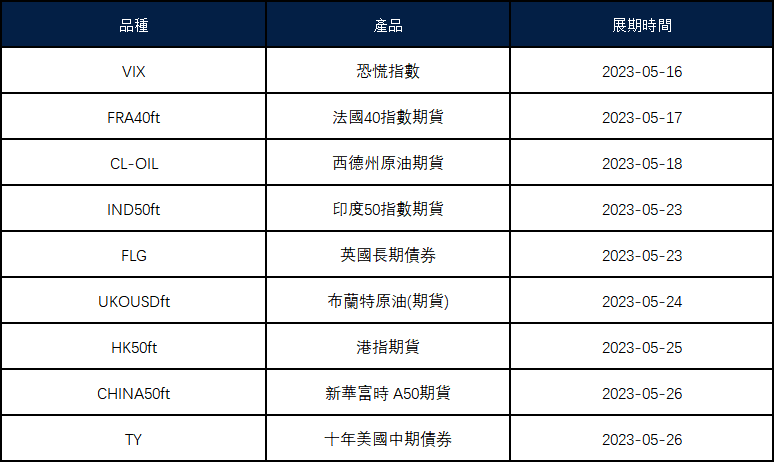
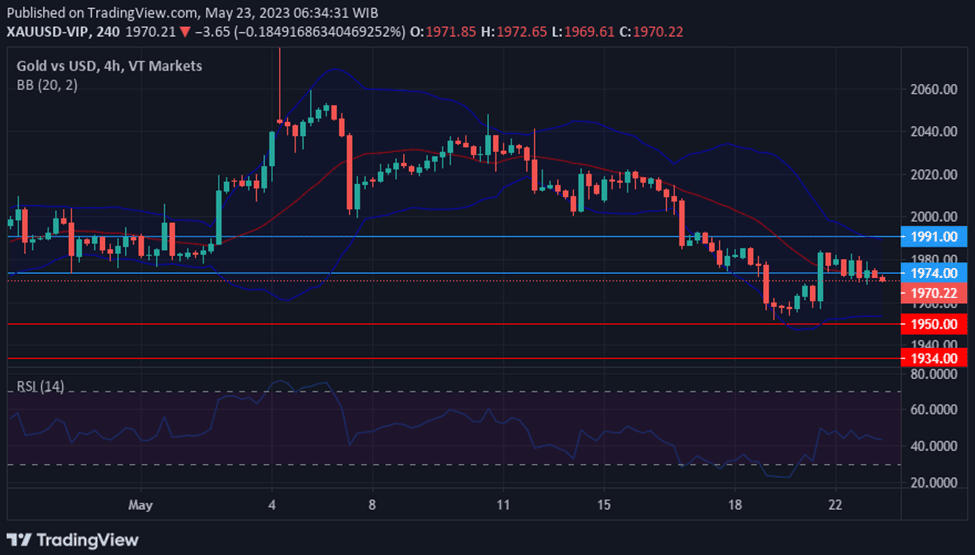
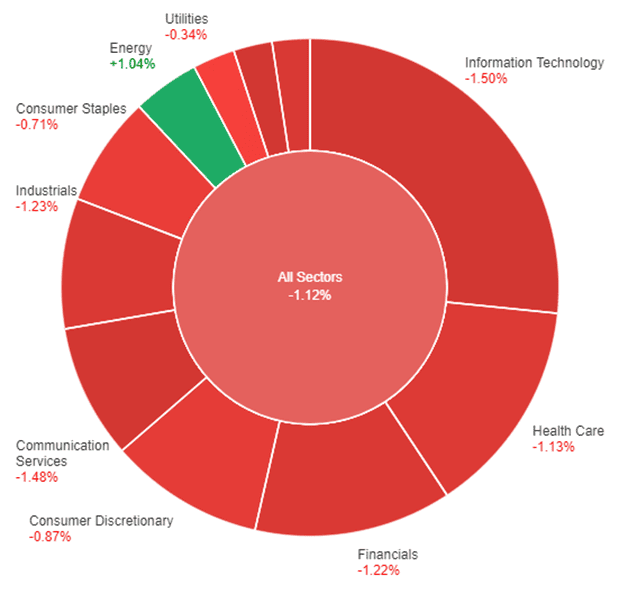
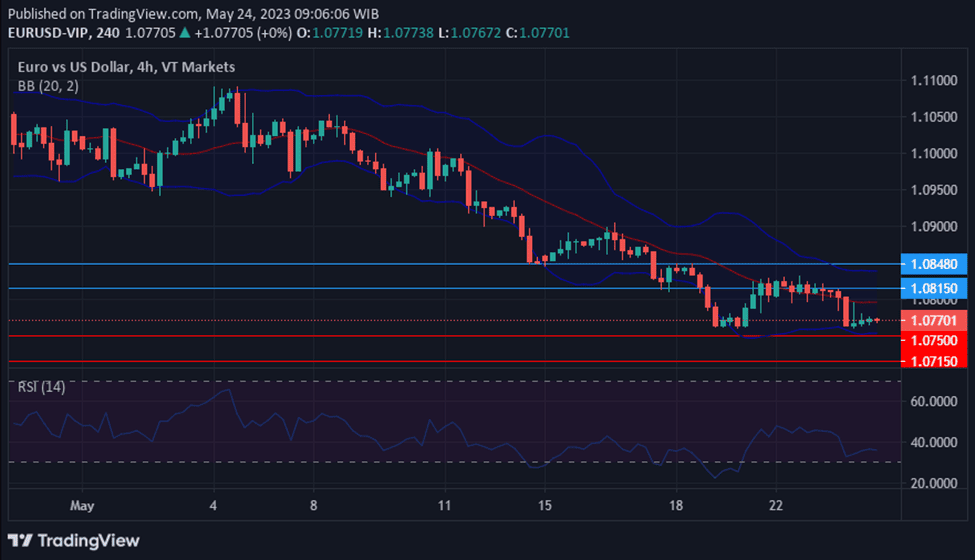
Forex is a short term for “foreign exchange,” which means changing one currency to another.
Let’s say you’re travelling from France to the United States. You’ll need to change your euros to US dollars. When you go to the bank, you’ll see a big board with names of different currencies and numbers. This board shows exchange rates, which are the price of one currency compared to another. For instance, the exchange rate for €1 is $1.2.

Suppose you exchange €1000 for $1200 before your trip. This means you participated in the Forex market.
However, when you’re on vacation, you’ll notice that the exchange rate has changed, and now €1 is worth less in US dollars than when you exchanged your money. As a result, your €1000 is now worth only $1100 instead of $1200. This means your euros can buy fewer things in the United States than you initially thought.
In the financial world, Forex traders aim to profit from the changes in exchange rates by buying and selling currencies at the right time.
The Forex market is the world’s largest and most liquid financial market. It is estimated that the daily trading volume of the Forex market has reached $7.5 trillion USD. To put this into perspective, the stock market in the United States has a daily trading volume of around $400 billion USD, which is just a fraction of the Forex market’s volume.
To help you visualise just how big the Forex market is, imagine the world’s largest shopping mall on Black Friday, with millions of people buying and selling goods all at once. Now, imagine that happening every single day, 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, all over the world. That’s how big the Forex market is.
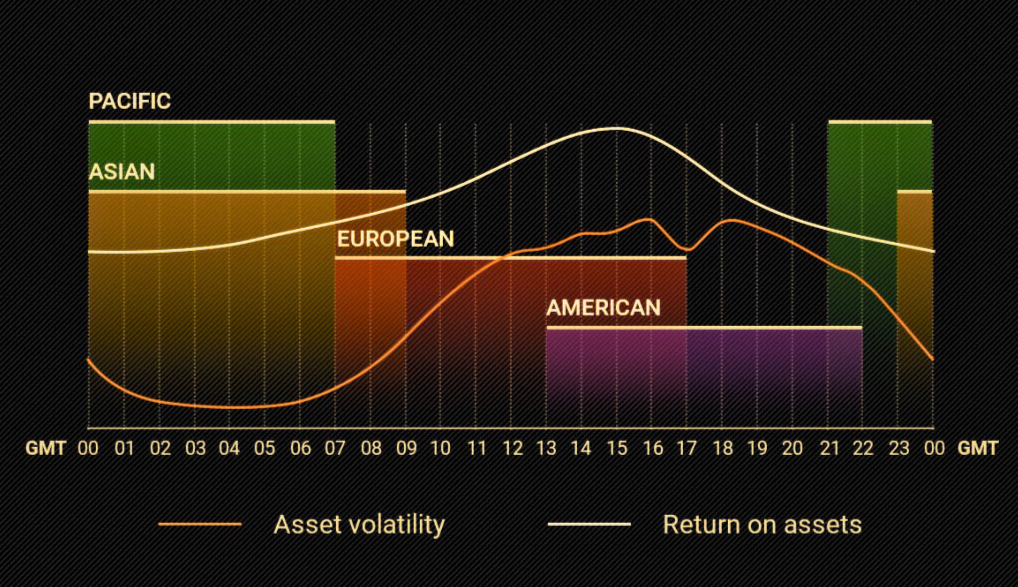
To facilitate trading around the clock, the Forex market has several financial centres located in different parts of the world, including New York, London, Tokyo, and Sydney. Each financial centre has its opening and closing hours, which overlap to create a continuous trading session.
For example, when it’s morning in New York, and the Forex market opens, it’s already afternoon in London, where the market is already open. This overlap in market hours allows traders to trade in multiple markets simultaneously and take advantage of the increased liquidity and volatility.
Forex plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade and investment by allowing businesses and individuals to exchange one currency for another. Without Forex trading, it would be difficult to conduct international transactions, as businesses and individuals would have to rely on their own country’s currency.
The Forex market is decentralised, meaning that it does not have a central location like the New York Stock Exchange or the London Stock Exchange. Instead, it operates through a global network of big commercial banks, central banks, multinational corporations, investors, hedge funds, and individual traders who buy and sell currencies electronically.
Commercial banks are the biggest players in the Forex market. They trade currencies for lots of different clients, such as other banks, big companies, and people who want to exchange money for their travels. When they trade currencies, they help to set the prices for all the other traders in the market. The big players that significantly influence the market are called market makers.
The Forex market operates through two main channels: the interbank market and the over-the-counter (OTC) market.
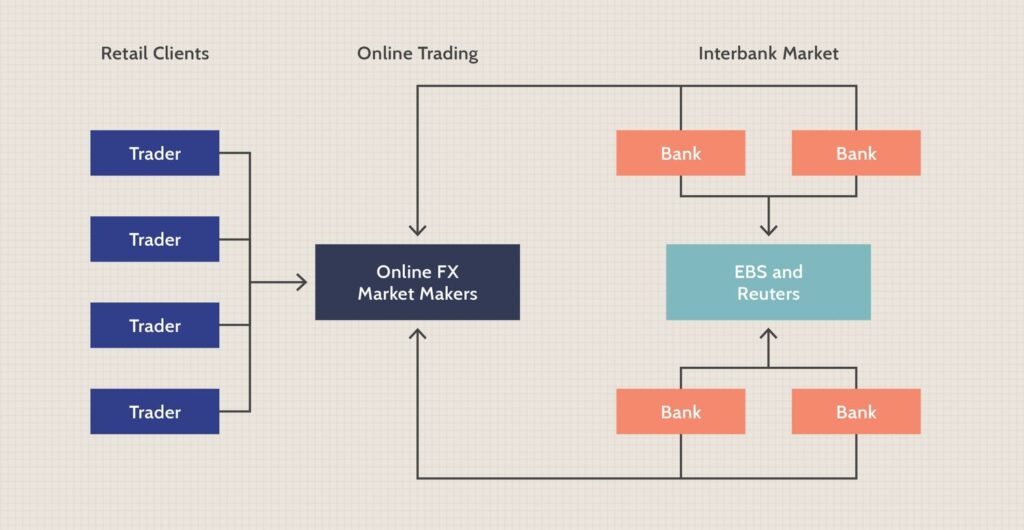
The interbank market is where banks and financial institutions trade currencies with each other, acting as both buyers and sellers. For example, if a bank needs to exchange US dollars for euros, it will turn to the interbank market to find another bank willing to sell euros and buy US dollars.
On the other hand, the OTC market is where trades are conducted directly between two parties without using a centralized exchange or clearinghouse. For example, if you’re travelling to another country and need to exchange your currency for the local currency, you might go to a currency exchange booth at the airport. The currency exchange booth acts as an OTC market maker, buying your currency from you and selling you the local currency at a markup.
Forex brokers like VT Markets play a crucial role in the Forex market by providing a platform for traders to buy and sell currency pairs. They act as intermediaries between traders and the market, executing trades on behalf of their clients.
As a broker’s client, you have the opportunity to earn profits by speculating on the movement of currency pairs. Brokers also offer various tools and resources to help traders make informed decisions, such as market analysis, educational materials, and trading signals.
Choosing a reputable and regulated broker is important, as the Forex market is known for its volatility and potential risks. However, with the right knowledge and strategy, trading Forex can be a lucrative opportunity for those willing to put in the effort to learn and practice.
Summary:
- Forex means “foreign exchange” and involves changing one currency to another.
- Exchange rates are the prices of one currency compared to another and fluctuate constantly in response to various economic and political factors.
- Forex traders aim to profit from changes in exchange rates by buying and selling currencies at the right time.
- The Forex market is the world’s largest and most liquid financial market, with a daily trading volume of $7.5 trillion USD.
- The Forex market operates through a global network of big commercial banks, central banks, multinational corporations, investors, hedge funds, and individual traders who buy and sell currencies electronically.
- The Forex market is decentralised and operates through two main channels: the interbank market and the over-the-counter (OTC) market.
- Forex brokers play a crucial role in the Forex market by providing a platform for traders to buy and sell currency pairs.